


Next: Code Design and Implementation
Up: Parallel Tempering in Monte
Previous: Complex Liquids: Water
This project has three major goals:
 Design, implement, and test a standalone MC code that is robust, extensible, and capable of performing PT as well as traditional Metropolis MC.
Design, implement, and test a standalone MC code that is robust, extensible, and capable of performing PT as well as traditional Metropolis MC.
 Implement an efficient parallelization scheme for the PT algorithm. Naive implementation of PT on parallel processors is dramatically inefficient, resulting in
Implement an efficient parallelization scheme for the PT algorithm. Naive implementation of PT on parallel processors is dramatically inefficient, resulting in 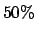 or more idle processor time [9]. This is because, in general, replicas run at lower temperature require more computational effort. Implementation of a job scheduler that manages and distributes replica runs over the available processors makes the method ideally efficient.
or more idle processor time [9]. This is because, in general, replicas run at lower temperature require more computational effort. Implementation of a job scheduler that manages and distributes replica runs over the available processors makes the method ideally efficient.
 Study the efficiency of PT in simulations of liquid water. Water is a glassy, complex liquid [10,11], and typical MC simulations require millions of MC steps to evolve the system into an uncorrelated configuration. We will use the TIP5P empirical potential, a rigid five-site geometry parametrized for classical MC simulations [12].
Study the efficiency of PT in simulations of liquid water. Water is a glassy, complex liquid [10,11], and typical MC simulations require millions of MC steps to evolve the system into an uncorrelated configuration. We will use the TIP5P empirical potential, a rigid five-site geometry parametrized for classical MC simulations [12].
John Gergely
2006-05-12