Drop
Manipulation Methods
•
Asymmetric horizontal vibration
Mettu, S. & Chaudhury,
M.K. Motion of Liquid Drops on Surfaces Induced by Asymmetric Vibration: Role
of Contact Angle Hysteresis. Langmuir 27, 10327-10333 (2011).
–
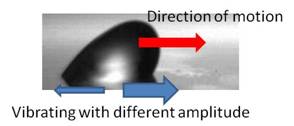 Vibrating a drop back and forth with
different amplitude induces its motion toward direction with larger substrate
displacement.
Vibrating a drop back and forth with
different amplitude induces its motion toward direction with larger substrate
displacement.
•
Surfaces with gradient wetting properties
Langley, K.R. & Sharp, J.S. Microtextured Surfaces with Gradient Wetting Properties. Langmuir 26, 18349-18356 (2010).
–
Patterned
surfaces with microwrinkled surface structures were
prepared by thermally evaporating thin aluminum (10 - 300 nm thick) (Al) layers
onto thick prestrained layers of a silicone elastomer.
–
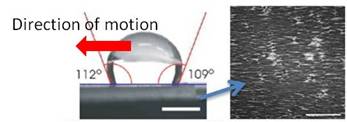 On this textured surface, sessile water
droplets were found to have different contact angles depending upon their
position.
On this textured surface, sessile water
droplets were found to have different contact angles depending upon their
position.
–
Droplets
under vibration tend to move down the wetting gradient from regions of high to
low interfacial energy. (larger contact angle side)
•
External electric field
Shi, L.T., Jiang, C.G., Ma, G.J. & Wu,
C.W. Electric field assisted manipulation of microdroplets
on a superhydrophobic surface. Biomicrofluidics
4, 041101 (2010).
–
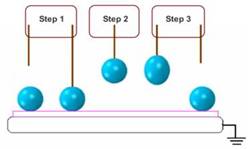 Droplets were first picked up onto a
hydrophilic needle, transported from one location to another, and finally
released under the action of an electric field force.
Droplets were first picked up onto a
hydrophilic needle, transported from one location to another, and finally
released under the action of an electric field force.